Difference Between Apoplast and Symplast Definition, Process, Characteristics
Apoplast and symplast are two pathways used by water to travel from the root hair cells to the xylem of the root. They are very much the same but they too differ in many ways. Table of Contents Apoplast Symplast What is the use of the symplast of the root cortex? The table below shows the differences between Apoplast and symplast.
Apoplast Difference between Apoplast and Symplast
Apoplast and symplast are two separate pathways in plants that initiate the passage of water along with ions from root hair via root cortex to xylem elements. These routes may exist either simultaneously or separately having different rates. Let us have a detailed look at apoplast and symplast and the difference between the two.
Apoplast Difference between Apoplast and Symplast
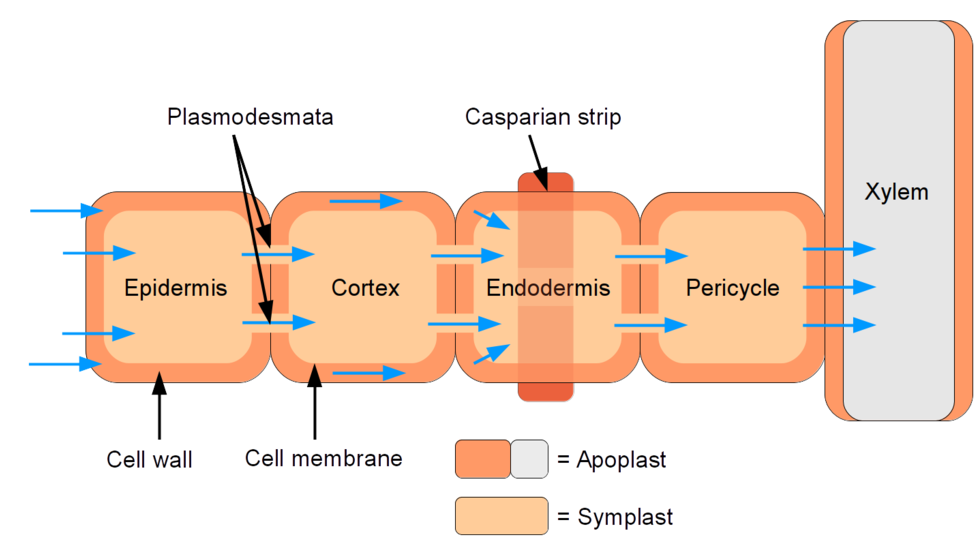
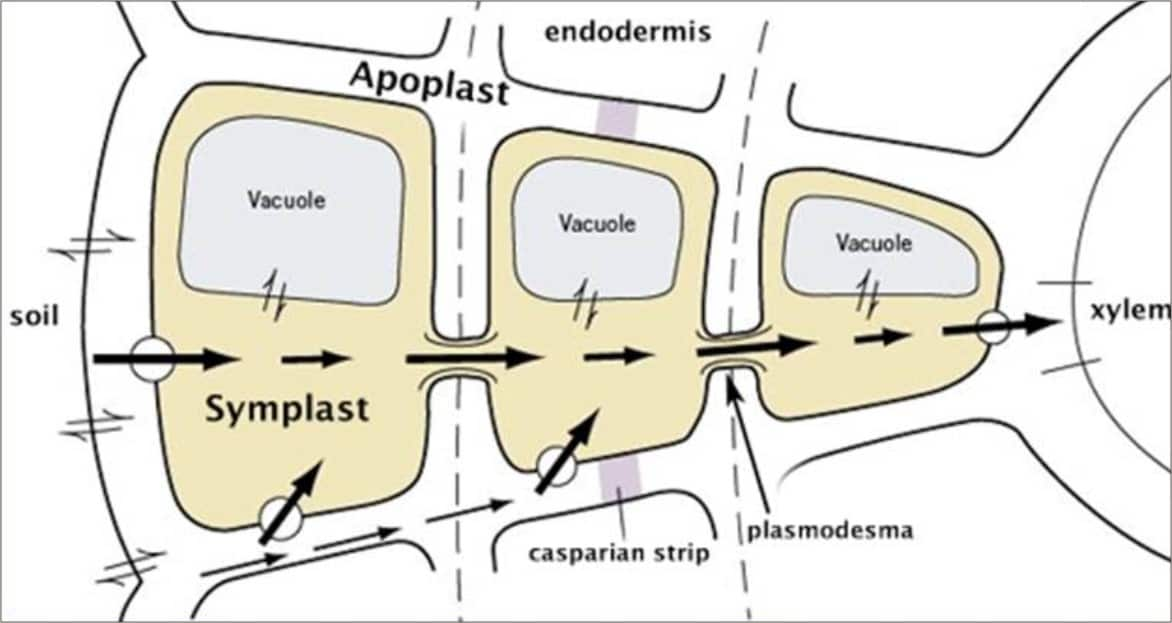
To distinguish the living symplast from the dead apoplast, Munch invented the term "apoplast" in 1930. Inside the plant, the apoplast is the outer space of the plasma membrane, which allows the material to freely diffuse and is interrupted by the Casparian strip in roots. Apoplast Pathway

Mechanism of water transport by apoplastic and symplastic... Download Scientific Diagram
Nowadays, the apoplast is defined as the intercellular space filled with gas and water, contained between cell membranes, the interfibrillar and intermicellar space of the cell walls, and the xylem extending to the rhizoplane and cuticle of the outer plant surface ( Figure 1 ).
Apoplast Difference between Apoplast and Symplast
Apoplast and symplast are the conduits of water and solutes throughout a plant's root system. Solutes are minerals (ions, amino acids) that are dissolved in water. Solutes can also include sugar.
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记7.2.6 The Sucrose Loading Mechanism翰林国际教育
The water and minerals have to cross different cell layers to reach the xylem. Apoplast and symplast pathways are the transport pathways adopted by water molecules. Although both are transport pathways, they differ from one another in various aspects. In the apoplast pathway, water moves through the cell walls and intercellular spaces without.

Water Transport in Plants Exchange and Transport Ep 15 Zoë Huggett Tutorials
Apoplast and symplast are two distinct pathways in plants that enable the transfer of water and ions from the root hair, through the root cortex, to the xylem elements. These routes can either exist together or separately, and they can have different rates of operation.
PPT Ch. 35(structure) Ch. 36(function) Roots and stems absorption and transport PowerPoint
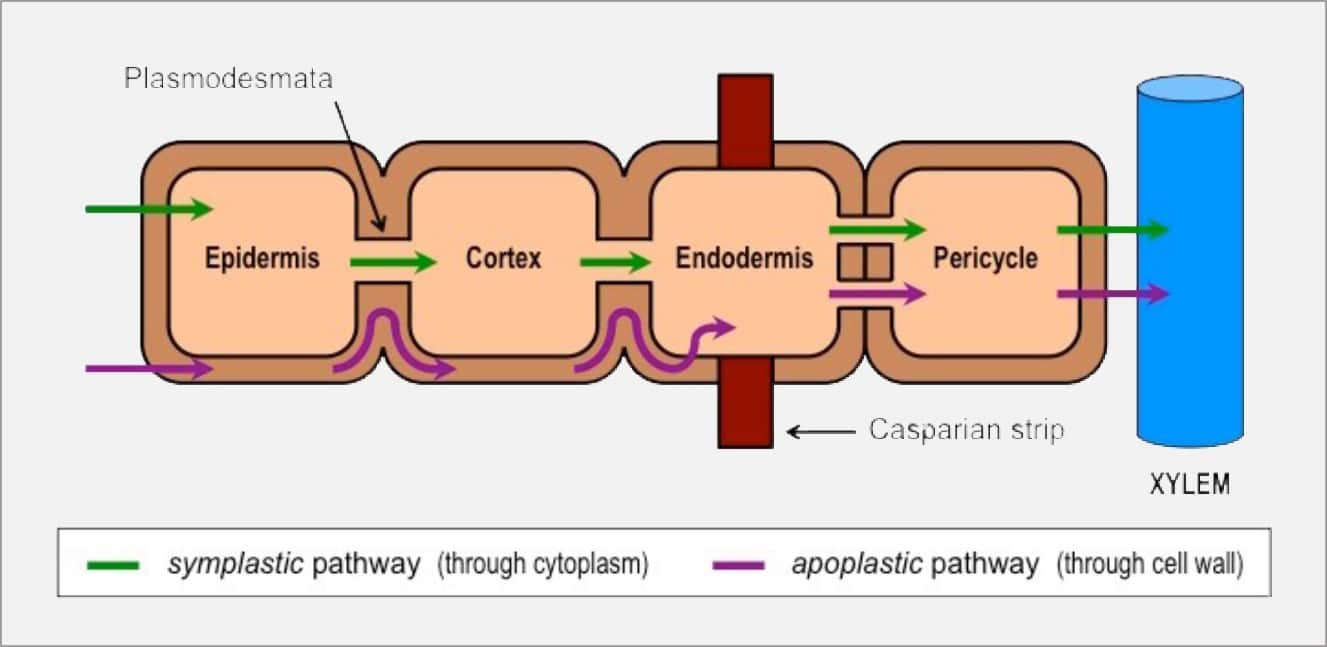
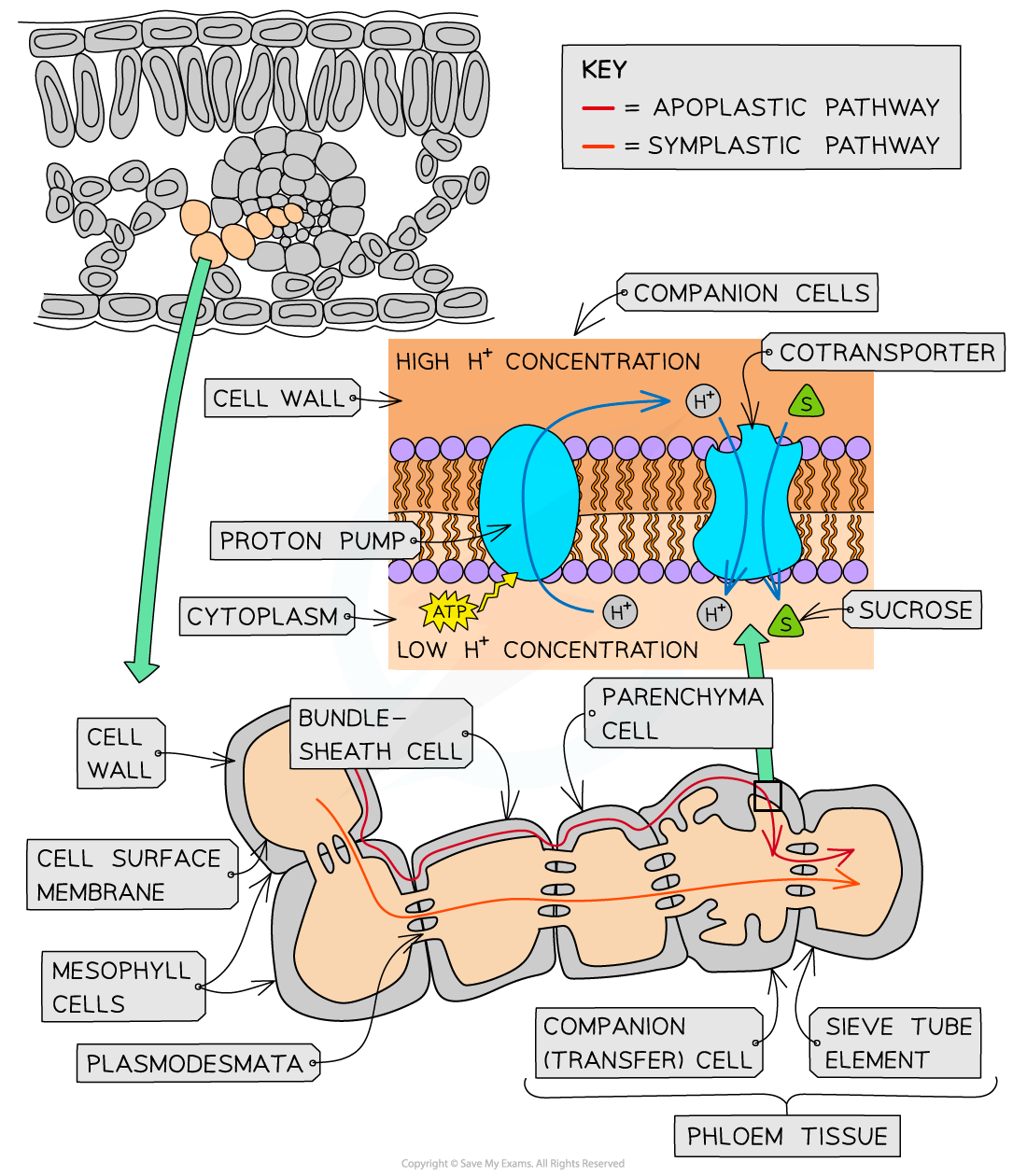
The apoplastic pathway: It provides the movement of water through the cell wall and other intercellular spaces. The apoplast, which is also called a cell wall is present on the outer side of the cell. The symplastic pathway: It provides the movement of water from one cell to another cell by plasmodesmata.
PPT Plant Organs Roots PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID366376
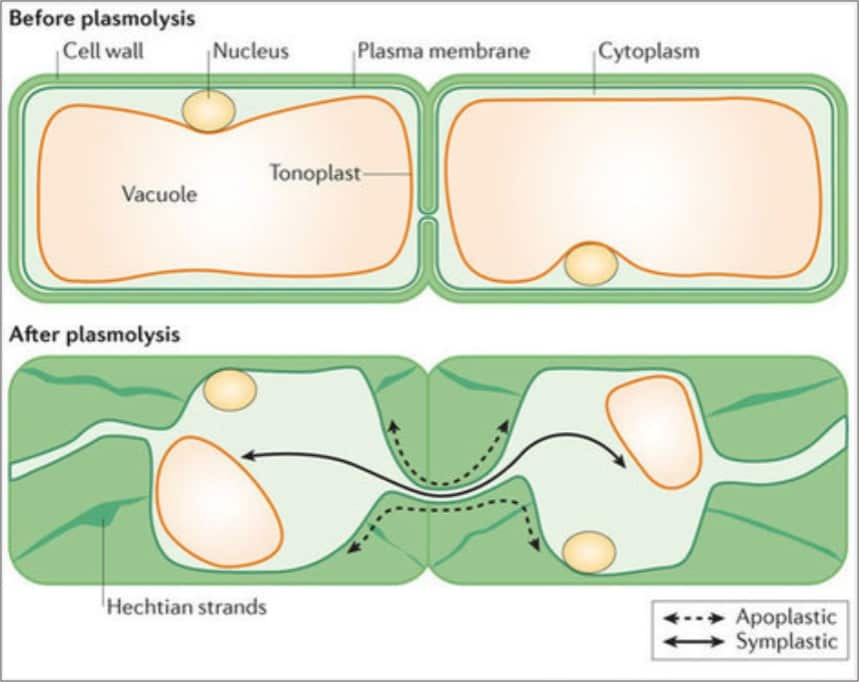
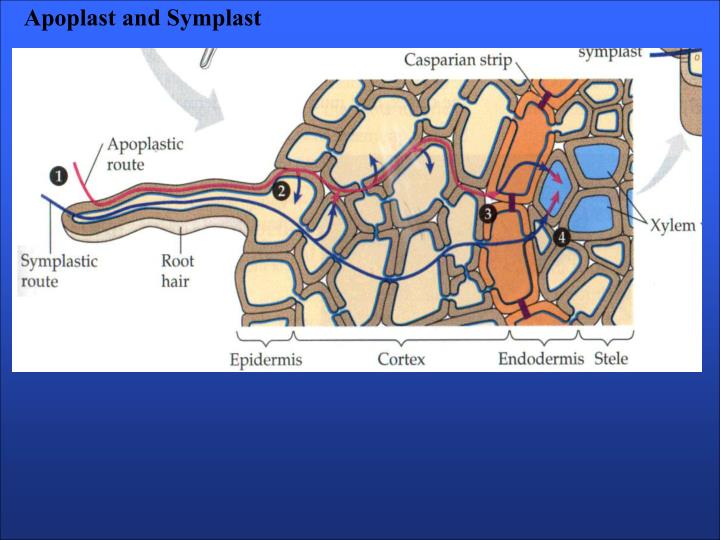
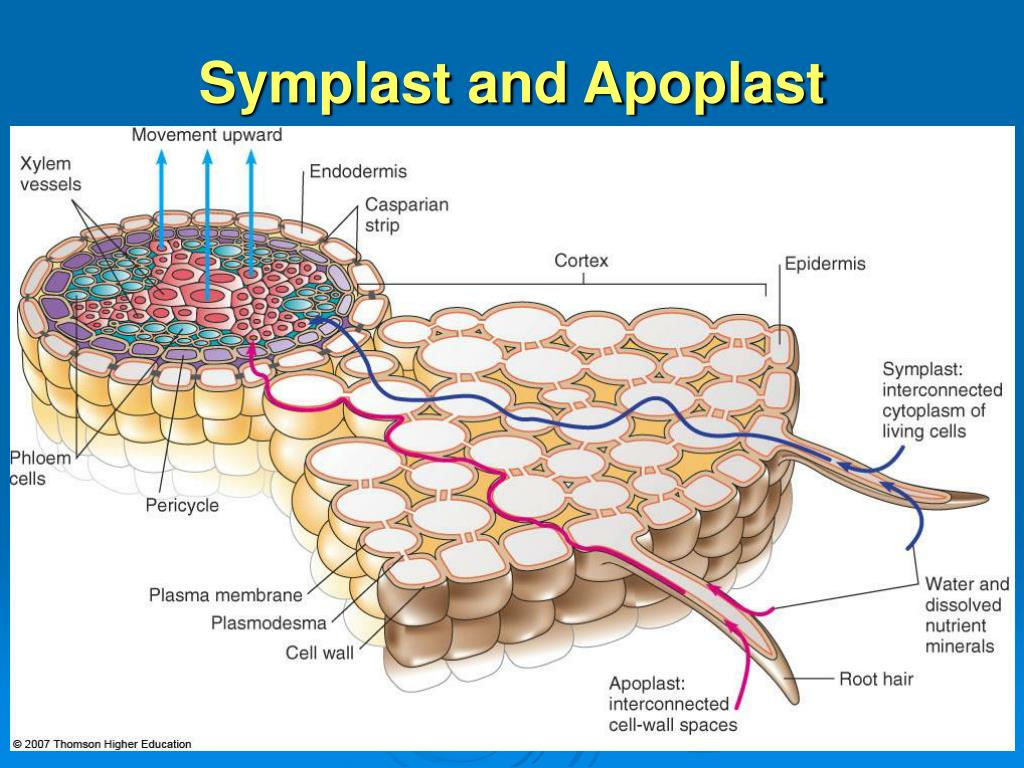
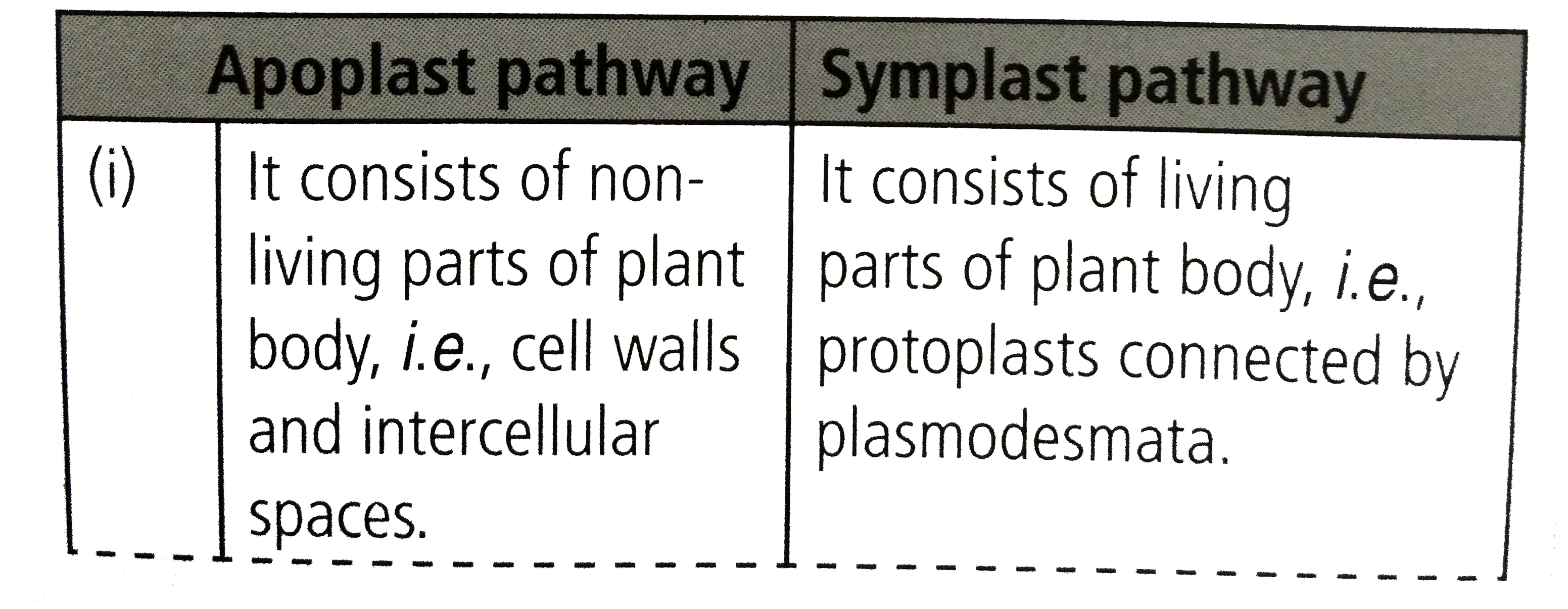
The symplast of a plant is the region enclosed by the cell membranes, within which water and solutes can diffuse freely. By contrast the apoplast is any fluid-filled space within the cell wall and extracellular space. [1] Neighbouring cells are interconnected by microscopic channels known as plasmodesmata that traverse the cell walls.

Diagrammatic representation of apoplastic and symplastic ion transport... Download Scientific
Apoplast and symplast are the two routes by which the water travels from root hair cells to the xylem of the root. In the apoplastic route, water moves through the cell walls and the intracellular spaces of the root cortex. In symplastic route, water moves through the protoplasts of the root cortex.
Apoplast/symplast pathway is a system of interconnected protoplast.
The Apoplast pathway is the path in which the water is moving between the intercellular spaces. The Apoplast includes the non-living spaces between cells and the cell membrane. Both pathways are involved in the movement of water across the root. Water flows via the Apoplast in the cortex.
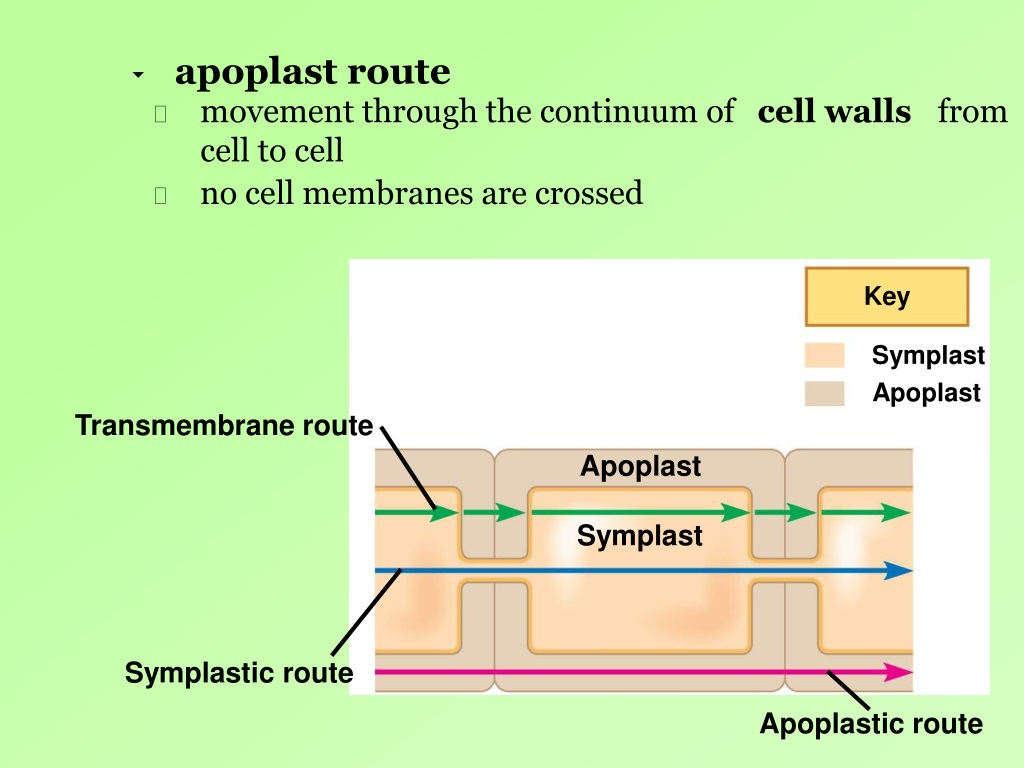
PPT Chapter 36 Transport in Vascular Plants PowerPoint Presentation ID9638517
3. Disease Resistance. Finally, the choice between apoplast and symplast can also impact a plant's ability to resist disease. The apoplast pathway can be more susceptible to pathogen invasion, while the symplast pathway can provide a more secure route for nutrient and water transport.

Apoplast and symplast pathway YouTube
Pathways of Water Movement. Water can move through the roots by three separate pathways: apoplast, symplast, and transmembrane (transcellular). In the apoplast pathway (apoplastic route), water moves through the spaces between the cells and in the cells walls themselves.In the symplast pathway (symplastic route), water passes from cytoplasm to cytoplasm through plasmodesmata (Figure.
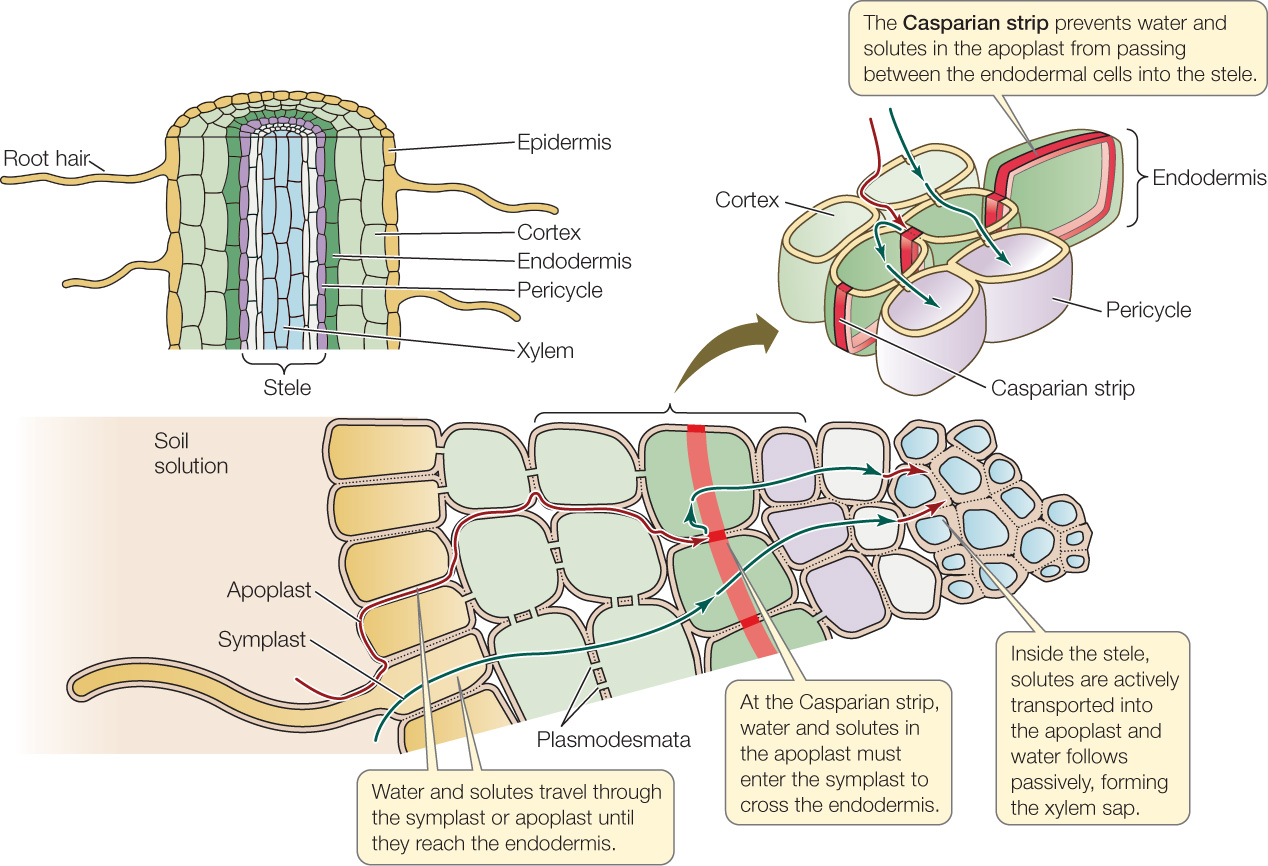
Figure 25.11
The apoplast route is the fully permeable route in which the water movement occurs in passive diffusion. Whereas the symplast is a selectively permeable route in which the water movement occurs by osmosis. The endodermis prevents the water and any solutes dissolved in water from passing through this layer via the apoplast pathway.

What is apoplast movement in plants?
(April 2023) The apoplast is the extracellular space outside of plant cell membranes, especially the fluid-filled cell walls of adjacent cells where water and dissolved material can flow and diffuse freely. Fluid and material flows occurring in any extracellular space are called apoplastic flow or apoplastic transport.

Apoplast and symplast. Helpful to NEET, CSIR and University students. YouTube
The apoplast includes everything outside the plasma membrane of living cells and consists of cell walls, extracellular spaces, xylem, phloem, and tracheids. The symplast, in contrast, consists of the entire cytosol of all living plant cells and the plasmodesmata - which are the cytoplasmic channels interconnecting the cells.