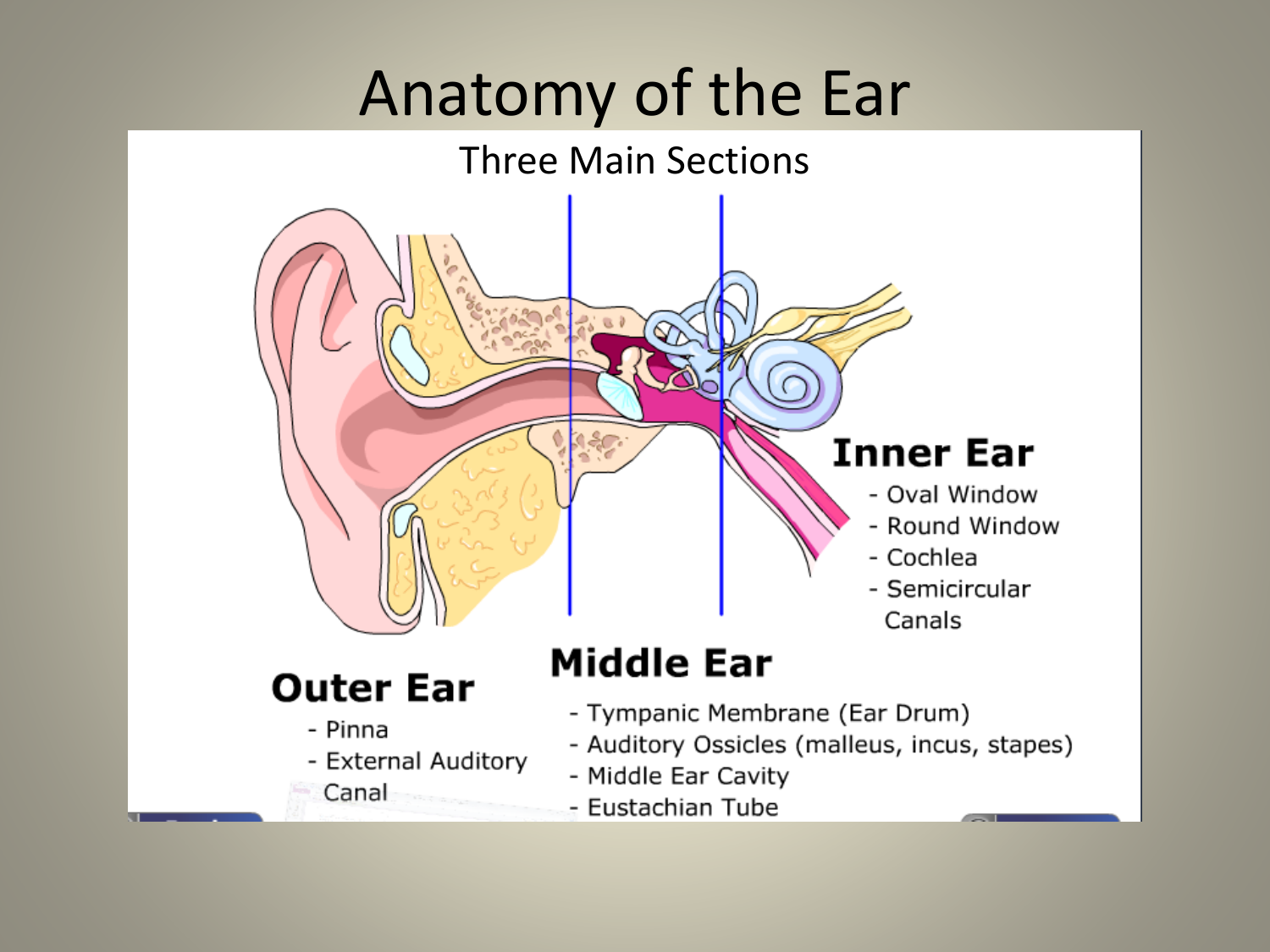
Anatomy of the Ear
The ear also helps in balancing the body. The human ear allows us to feel the effect of gravity that is known as stationary balance and it also helps to feel the acceleration that is known as dynamic balance. The utricle and saccule provide a static balance. Dynamic balance is provided by semi-circular canals.

Ears and hearing How do they work?
A labelled cross-sectional diagram of the human ear. Summary [ edit] All translations [ edit] Translations added to this section should be free of copyright claims (either CC0 or public domain). Malleus ≅ malleus (Q319636) Malleus Incus ≅ incus (Q497385) Incus Stapes ≅ stapes (Q499897) Stapes oval window ≅ oval window (Q2301793) oval window

Human ear anatomy. Ears inner structure, organ of hearing ve (1000410) Infographics Design
Overview Your outer ear and middle ear are separated by your eardrum, and your inner ear houses the cochlea, vestibular nerve and semicircular canals (fluid-filled spaces involved in balance and hearing). What is the ear? Your ears are organs that detect and analyze sound. Located on each side of your head, they help with hearing and balance.

Labeled Diagram Of The Interior Of A Human Ear For Reference stock vector art 185868456 iStock
The human ear consists of three parts: External ear Middle ear Internal ear Human Ear Parts The human ear parts are explained below: External Ear The external ear is further divided into the following parts: Auricle (Pinna) The auricle comprises a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by a layer of skin.

How The Ear Works
The auricle or pinna is the most visible part of the outer ear and what most people are referring to when they use the word "ear." Middle ear: Three tiny bones — the malleus, incus, and.

Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review Ear anatomy, Middle ear, Human anatomy and physiology
1. External Ear: It comprises a pinna, external auditory meatus (canal) & tympanic membrane. (i) Pinna: ADVERTISEMENTS: The pinna is a projecting elastic cartilage covered with skin. Its most prominent outer ridge is called the helix.

Diagram Of A Human Ear Vector Illustration Of Diagram Of Human Ear Anatomy Royalty Free Ear
1: Diagram showing the structure of the human ear, detailing the parts. | Download Scientific Diagram Figure 2 - uploaded by Benjamin Gorman Content may be subject to copyright. 1:.

Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection & Pain Causes & Treatment
Diagram of Ear Human ear is a sense organ responsible for hearing and body balance. The outer ear receives the sound waves and transmits them down the ear canal to the eardrum. This causes the eardrum to vibrate and sound is produced. The diagram of the ear is important from Class 10 and 12 perspectives and is usually asked in the examinations.

Anatomy of the Ear [4]. Download Scientific Diagram
human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). Understand the science of hearing and how humans and other mammals perceive sound How humans and other mammals perceive sound.
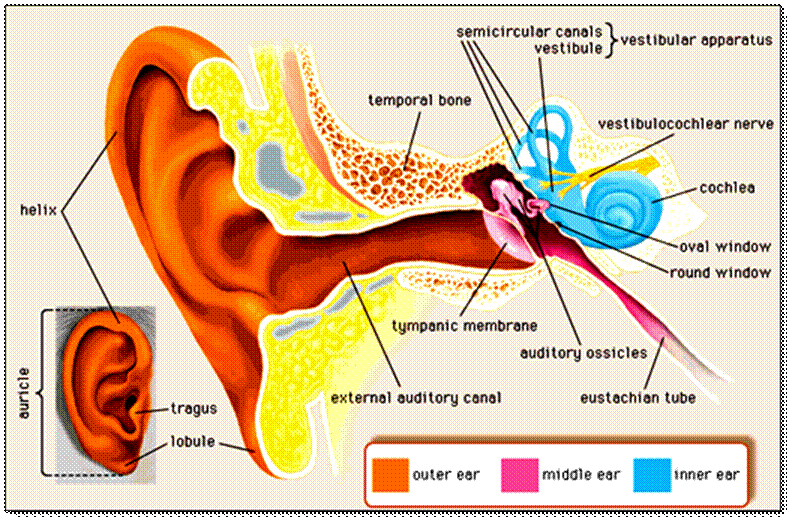
Anatomy of Human Ear
Labelled Diagram of Ear The Ear is composed of various parts which have been described below. Outer Ear: The outer Ear has two parts pinna or auricle and Ear canal Pinna or auricle: This part is present outside of the middle ear and pinna collects the sound waves and transmit them to the Ear cannal.

Human Ear Anatomy Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear Problems
Ear Anatomy - Inner Ear. Ear Anatomy Schematics. Ear Anatomy Images. Chapter 4 - Fluid in the ear. Fluid in the ear Discussion. Fluid in the ear Outline. Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes. Fluid in the ear Images. Chapter 5 - Traveler's Ear.

Human Ear Anatomy How Hearing Works Connect Hearing
1/4 Synonyms: External auditory meatus, External acoustic pore , show more. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. It is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. The main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance.
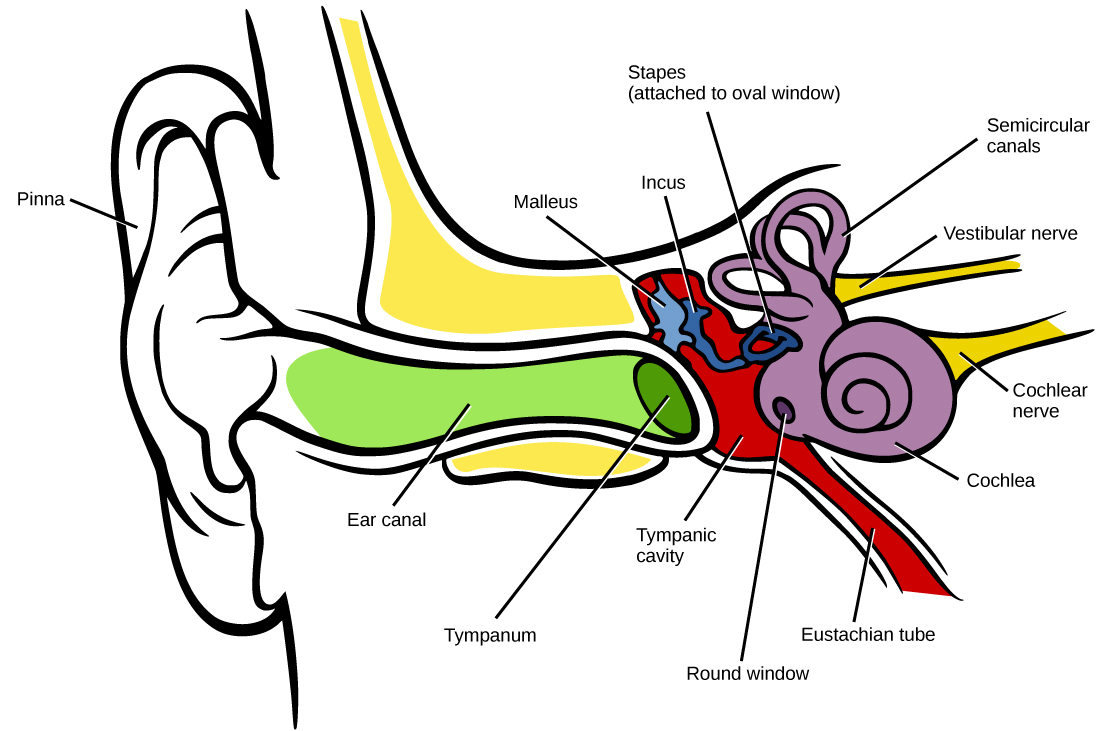
3 Things to Know About the Signal Path of the Auditory System — Pro Audio Files
1 The organ of corti is a structure present in (a) external ear (b) middle ear (c) semi-circular canal (d) cochlea Q 2 Draw a labelled diagram of the inner ear. Name the part of the inner ear that is responsible for static balance in human beings. Q 3 Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the human ear.
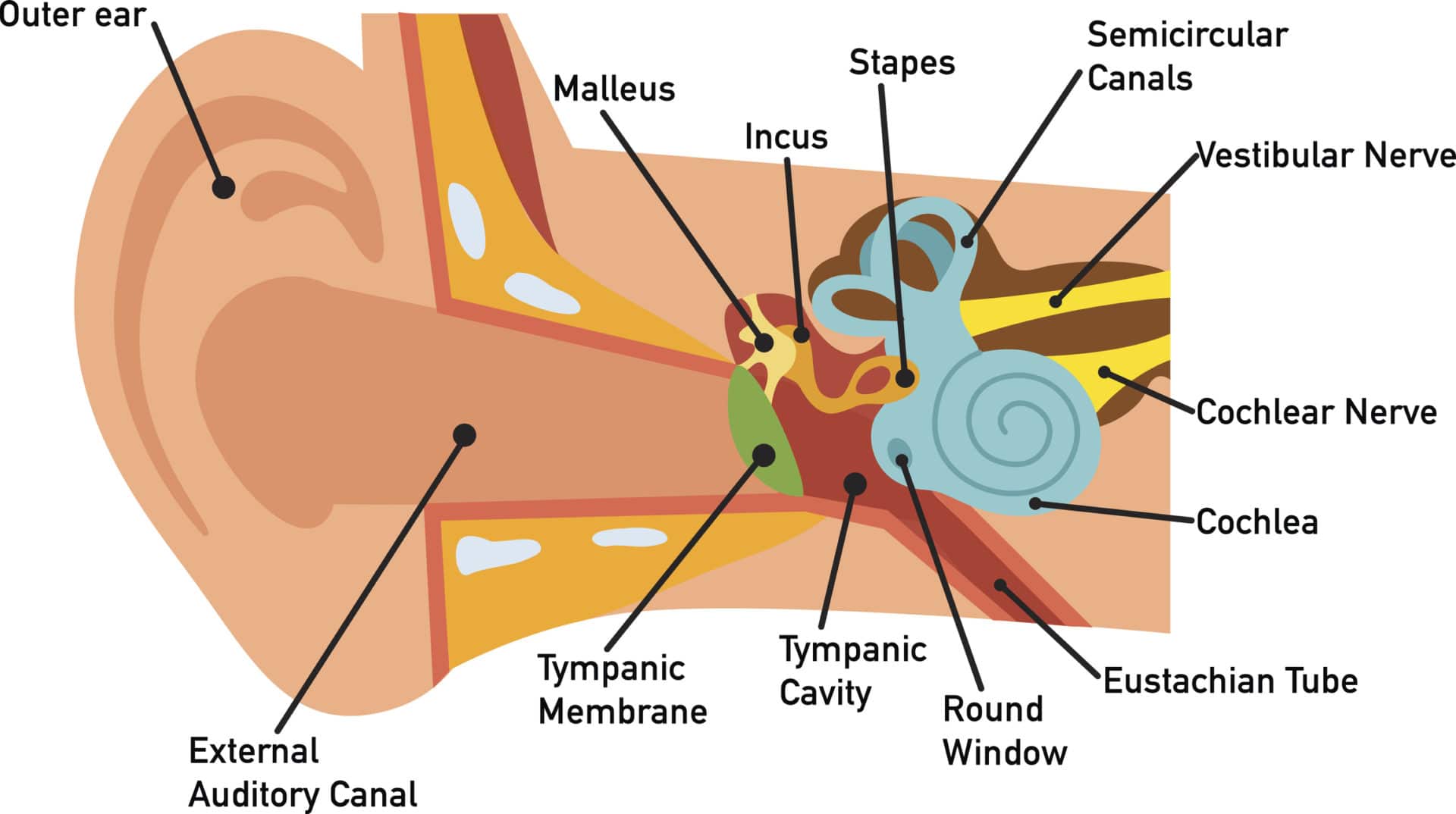
How You Hear Northland Audiology
The Human Ear www.TurnItToTheLeft.com. If the noise is too loud, walk away, turn it down (Turn it to the Left), or use ear plugs. pinna ear canal ear drum hammer anvil stirrup Eustachian tube (connects to the nose) cochlea semicircular canals nerves (connect to the brain) Directions: Color in the diagram below using a different color for.
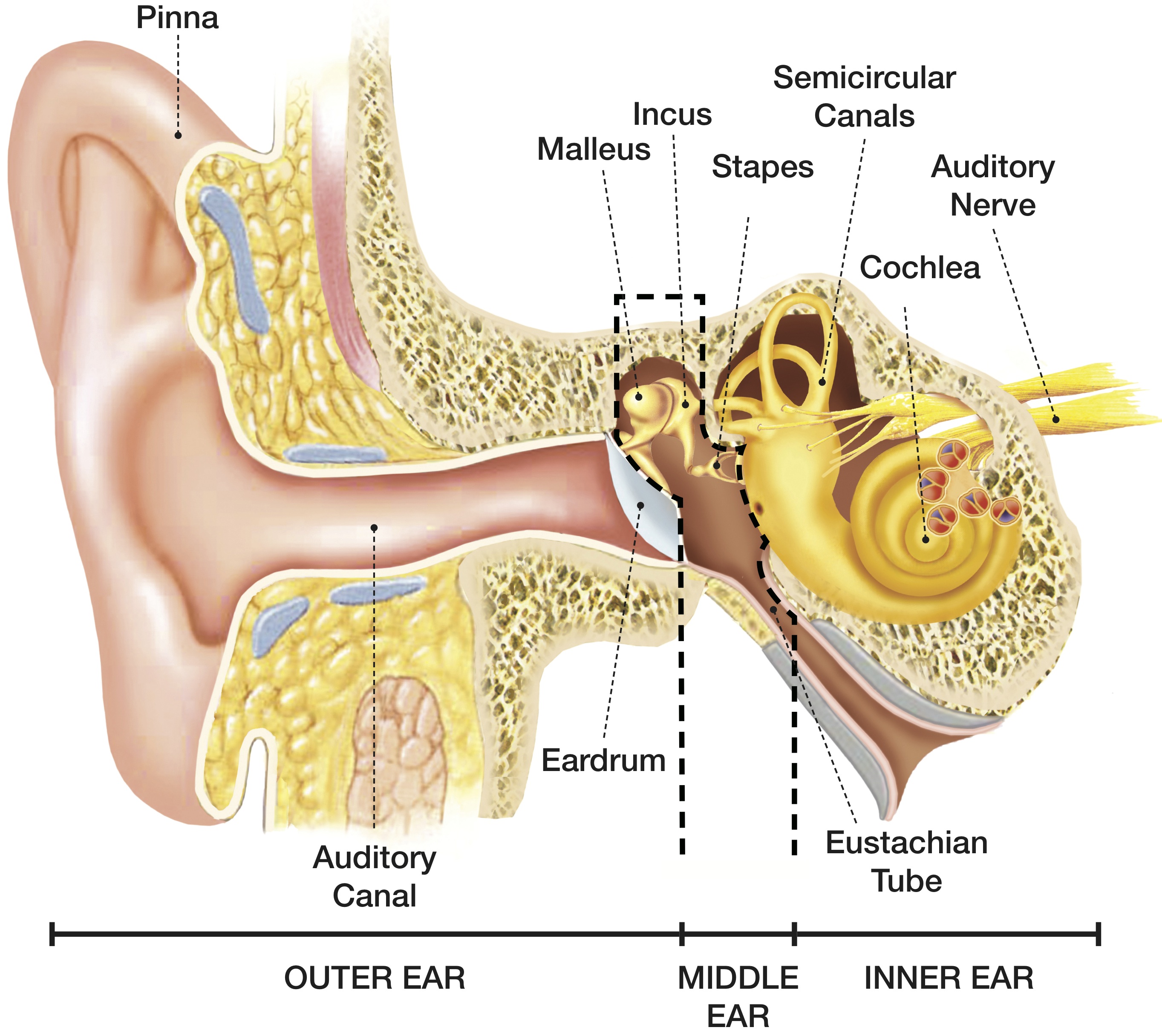
How We Hear Hearing Associates, Inc.
Download a free printable outline of this video and draw along with us: https://artforall.me/video/how-to-draw-human-earThank you for watching. Please subsc.

Alila Medical Media Human ear anatomy, labeled diagram. Medical illustration
Human ear. The ear is divided into three anatomical regions: the external ear, the middle ear, and the internal ear (Figure 2). The external ear is the visible portion of the ear, and it collects and directs sound waves to the eardrum. The middle ear is a chamber located within the petrous portion of the temporal bone.