
Entity Framework Core A Full Tour
Adding the Index Attribute to one or more properties of an Entity will cause Entity Framework Core to create the corresponding index in the database. So, in Entity Framework Core, the Index attribute defines indexes on columns in your database to improve query performance. An index allows the database to efficiently look up rows based on the.

Entities relationships with Entity Framework Core 3 by Andre Lopes
Entity Framework Code First Fluent Api: Adding Indexes to columns Ask Question Asked 12 years, 1 month ago Modified 3 years, 4 months ago Viewed 59k times 66 I'm running EF 4.2 CF and want to create indexes on certain columns in my POCO objects. As an example lets say we have this employee class:

20 Pros and Cons of Entity Framework 2023 Ablison
Index Attribute Entity Framework 6 provides the [Index] attribute to create an index on a particular column in the database, as shown below: class Student { public int Student_ID { get; set; } public string StudentName { get; set; } [Index] public int RegistrationNumber { get; set; } } By default, the index name will be IX_ {property name}.

1 entity framework core course by by Shailender chauhan
So, the InverseProperty attribute is a useful tool for explicitly specifying relationships in EF Core when conventions are insufficient or ambiguous. It helps ensure that the framework correctly interprets the relationships. In the next article, I will discuss NotMapped Attribute in Entity Framework Core with Examples.

Entity Framework 6.0.6 and 6 Console Application Example
Entity Framework 6 provides the [Index] attribute to create an index on a particular column in the database. If you are using an earlier version of Entity Framework, then the Index Attribute will not work. It is also possible to create an index on one or more columns using the Index Attribute.
Infographic An Introduction to Entity Framework
If we add the migration, we should see Entity Framework Core actually understands the attribute now and translate it to the migration file. GitHub Snippet. migrationBuilder.CreateIndex ( name: "IX_Name", table: "ProductGroups", column: "Name"); So, when I run update-database to apply the migration, I see the indexes are created into the table.

Entity framework with autoincrement column Stack Overflow
This creates a unique index. [Index ("IX_Person_NameAndAge", 1)] public int Age { get; set; } [Index ("IX_Person_NameAndAge", 2)] public string PersonName { get; set; } This creates a composite index using 2 columns. To do this you must specify the same index name and provide a column order. Note: The Index attribute was introduced in Entity.
Entity Framework Core Tutorial Database First Tutorial
2 Answers Sorted by: 20 EF Core 5 In EF Core 5, the Index attribute should be placed on the class. See: MSDN [Index (nameof (Url))] public class Post { public int PostId { get; set; } public string Url { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } public DateTime PublishedOn { get; set; } }

ENTERPRISE SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS INC.
The simplest way to add an index is to by adding the [Index] attribute on the model class and specifying which columns should be included in the index. Here's an example of adding an index with a single column: using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; [Index (nameof (Name)) ] public class Movie { [Key.
Er Diagram Unique Attribute
Entity Framework 6 provides the Index attribute to create an index on a particular column in the database. public class Book {public int Id {get; set;}. Now in EF Core, the new Index attribute can be placed on an entity type to specify an index for one or more columns. [Index (nameof (Title), IsUnique = true)] public class Book

Index Attribute Using Entity Framework
108 Well 26.10.2017 Entity Framework 6.2 was officially released . It includes a possibility to define indexes with ease via Fluent API. Ho it is to use was already announced in the beta of 6.2. Now you can use the HasIndex () method, followed by IsUnique () if it should be an unique index. Just a small comparison (before/after) example:

Entity Framework integration with SQL Persistence • Sql Persistence
By default, indexes are created for foreign keys and alternate keys. You may wish to create indexes on other properties to speed up data retrieval.

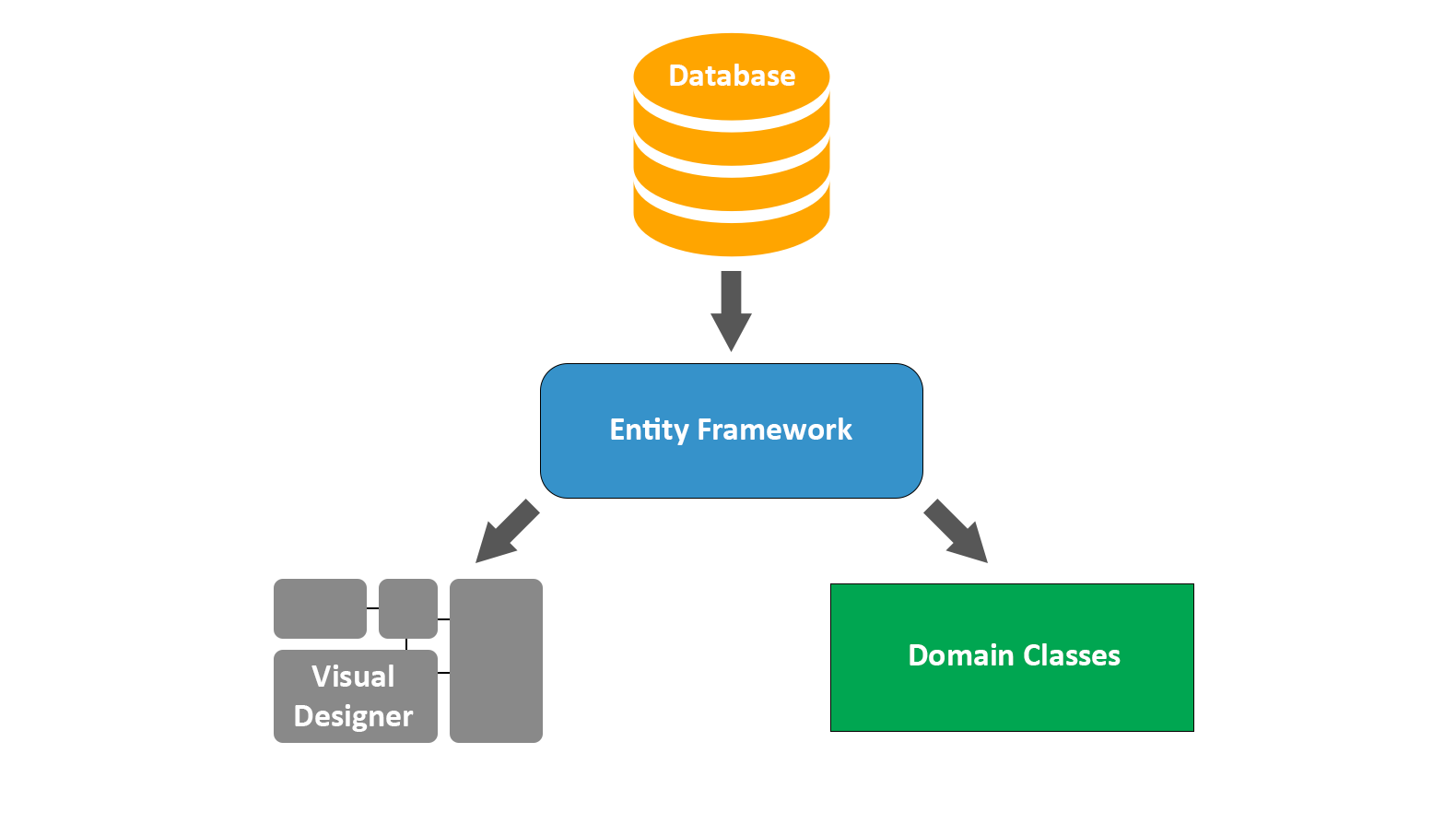
Infographic An Introduction to Entity Framework
Entity Framework Core Entity Properties Article 01/12/2023 6 contributors Feedback In this article Included and excluded properties Column names Column data types Required and optional properties Show 3 more Each entity type in your model has a set of properties, which EF Core will read and write from the database.

Best Entity Framework Online Courses, Training with Certification2022
Entity Framework Core Indexes Article 12/18/2023 10 contributors Feedback In this article Composite index Index uniqueness Index sort order Index naming and multiple indexes Show 3 more Indexes are a common concept across many data stores.
Entity Framework Core Tutorial
Definition Namespace: Microsoft. Entity Framework Core Assembly: Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Abstractions.dll Package: Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Abstractions v8.0.0 Specifies an index to be generated in the database. C# [System.AttributeUsage (System.AttributeTargets.Class, AllowMultiple=true)] public sealed class IndexAttribute : Attribute

Entity Framework Oakleafsd
EF Core Index Attribute The Entity Framework Core IndexAttribute was introduced in .NET 5 and is used to create a database index on the column mapped to the specified entity property. By default, indexes are created for foreign keys and alternate keys. You may wish to create indexes on other properties to speed up data retrieval.